10 Idea Frameworks | 매거진에 참여하세요
10 Idea Frameworks
#IdeaStruct #Framework #JTBD #FAB #ABC #XYZ
Having Trouble Structuring Your Ideas?
We’ve all had a brilliant idea flash through our minds—only to lose the moment because we couldn’t quite put it into words.
In planning, startups, marketing, content creation, and many other fields, a well-structured and clearly communicated idea is essential for actual execution.
That’s where idea structuring frameworks come in handy.
One of the most powerful, yet simple, formats is:
“To solve A, we do B in order to achieve C.”
Let’s explore several frameworks that allow you to neatly condense ideas into a single sentence with clear reasoning and justification.
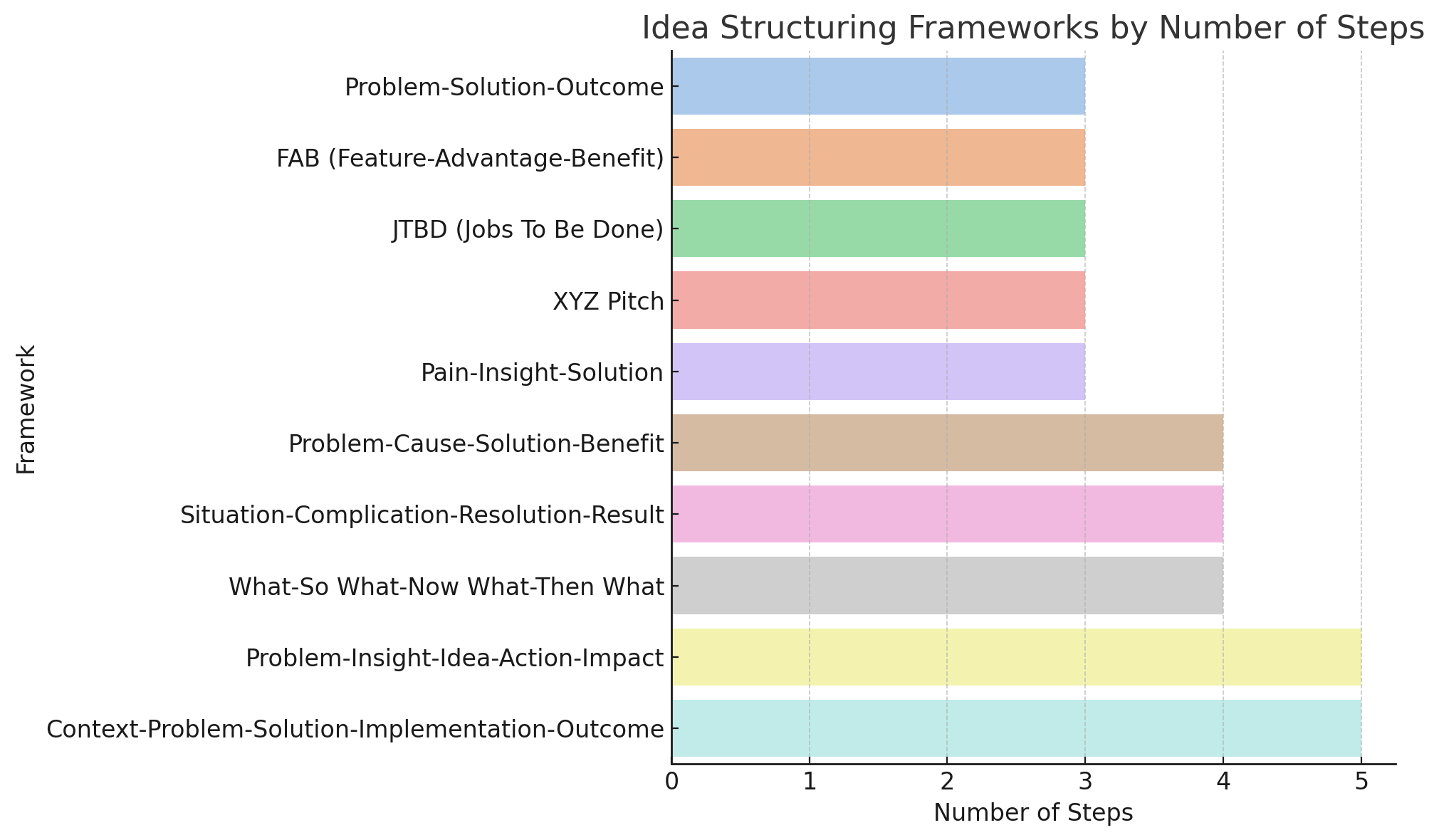
3-Stage Structures
1. Problem – Solution – Outcome
Format:
To solve A (problem), we do B (solution) to achieve C (result).
This is the most intuitive framework, commonly used in startup pitches, planning documents, and product descriptions.
- Example:
To solve job seekers' anxiety, we provide mentorship services from professionals to offer practical advice and build confidence.
- Strength: Simple and effective for communication
- Use Cases: Startup pitches, slogans, product descriptions
2. FAB (Feature – Advantage – Benefit)
What is the feature, what advantage does it offer, and what benefit does the user gain?
- Example:
The auto email summarizer (Feature) → saves reading time (Advantage) → helping users better manage their information load (Benefit)
- Strength: Great for product-focused descriptions
- Use Cases: Marketing, sales, content presentation
3. JTBD (Jobs To Be Done)
What "job" is the customer hiring this product to do?
- Format:
In situation A, to solve problem B, the user uses tool/service C.- Example:
Office workers subscribe to a 3-line summary newsletter on their morning commute to quickly catch up on the latest news.
- Strength: Deep insight from a user-centered perspective
- Use Cases: Service planning, UX design, marketing strategy
4. XYZ Pitch
Optimized for introducing startups.
- Format:
We help X (target user) do Y (task) by Z (solution).- Example:
We help college students explore careers by connecting them to industry professionals through a 1:1 platform.
- Strength: Instantly conveys who it's for and what it does
- Use Cases: Elevator pitches, slogans, business intros
5. Pain – Insight – Solution
Goes beyond listing problems by identifying hidden causes (insights) and connecting them to solutions.
- Format:
People suffer due to A.
The root cause is actually B.
We solve this with C.- Example:
Many worry about careers but avoid counseling.
Because they don’t know who to ask.
We solve this through a 1:1 mentor matching service.
- Strength: Combines persuasiveness with insight
- Use Cases: Reports, proposals, investor decks
4-Stage Frameworks
6. Problem – Cause – Solution – Benefit
This structure goes beyond linear thinking to identify root causes and tailor solutions accordingly.
- Problem: The apparent symptom or issue
- Cause: Underlying reasons or context
- Solution: Strategy targeting the cause
- Benefit: Anticipated positive outcomes
Example:
- Problem: User drop-off from the content feed has increased by 15%.
- Cause: The AI algorithm shows irrelevant content, causing overload.
- Solution: Improve personalization and filtering.
- Benefit: Higher content relevance → longer engagement time (estimated 20%↑), better satisfaction, improved subscription rates.
7. Situation – Complication – Resolution – Result
Inspired by McKinsey’s SCQA model, widely used in consulting for logical storytelling.
- Situation: The current observed state
- Complication: Emerging problem or challenge
- Resolution: The proposed fix
- Result: Post-resolution benefits
Example:
- Situation: 70% of students haven’t decided on careers by graduation.
- Complication: Counseling is too theoretical and not personalized.
- Resolution: 1:1 mentoring platform with real professionals.
- Result: Satisfaction rose (25%→88%), career decision rates improved, referrals increased.
8. What – So What – Now What – Then What
This reflection-driven framework is ideal for workshops, meetings, or strategy sessions.
- What: Objective observations
- So What: Significance of the data
- Now What: Actions to take next
- Then What: Anticipated changes
Example:
- What: Real-time feedback requests dropped by 40% over 3 months.
- So What: Reduced feedback = stalled work, unclear goals, mistrust.
- Now What: Introduce a feedback tool + dedicate 5 mins in weekly meetings.
- Then What: Improved communication, leadership growth, deeper engagement
5-Stage Frameworks
9. Problem – Insight – Idea – Action – Impact
Not just about solving problems, but gaining insight and turning it into action with tangible outcomes.
Used frequently in brainstorming, design thinking, and product planning.
- Problem: The user's pain point
- Insight: Hidden or underlying cause
- Idea: Creative solution
- Action: Specific features or activities
- Impact: Resulting change or effect
Example:
- Problem: Team productivity down 20% in 3 months
- Insight: Not just low motivation, but repetitive work and lack of feedback
- Idea: Break work into daily missions with instant feedback
- Action: Add “Daily Mission” feature to task manager + auto-feedback from leaders
- Impact: 33% productivity boost, 92% satisfaction in daily reports
10. Context – Problem – Solution – Implementation – Outcome
Widely used in proposals and planning documents. Presents a complete logical flow.
- Context: Background or market environment
- Problem: Key challenge within that context
- Solution: Strategy to solve it
- Implementation: Specific plans and steps
- Outcome: Projected results and ripple effects
Example:
- Context: High churn in competitive B2B SaaS market
- Problem: New users fail onboarding → leave early
- Solution: 7-day onboarding scenario + feature suggestions in first 3 days
- Implementation: Behavioral triggers, tutorials, automated welcome emails
- Outcome: Onboarding completion up (52%→81%), churn down 26%, potential conversion boost
Recommended Frameworks by Purpose
Purpose | Recommended Frameworks |
|---|---|
Clear message delivery | Problem–Solution–Outcome, XYZ Pitch |
Emphasizing feature value | FAB |
User-centered design | JTBD |
Logical storytelling | Situation–Complication–Result |
Deep problem analysis | Pain–Insight–Solution, 5-stage models |






